Today, the Global Commission on HIV and the Law finally issued its long-awaited report, 'HIV and the Law: Risks, Rights and Health.' It was well worth the wait.
"Fundamentally unjust, morally harmful, and virtually impossible to enforce with any semblance of fairness, such laws impose regimes of surveillance and punishment on sexually active people living with HIV, not only in their intimate relations and reproductive and maternal lives, but also in their attempts to earn a living."
That's how the Chapter 2 of the report, focusing on the criminalisation of HIV non-disclosure, potential exposure and non-intentional transmission begins. The rest of the chapter pulls no punches either.
Of course, the Global Commmission, and the report itself, cover much more than HIV criminalisation, and it pulls no punches recommending repeal of punitive laws impacting consensual same-sex sex, sex work, drug use and patent laws affecting access to HIV treatment. However, since this blog - and the focus of my work - is specifically about HIV criminalisation I'm only going to focus on the six pages in the report (and five pages of references) that specifically addresses this issue.
 |
| Five recommendations on HIV criminalisation: click on image to enlarge |
To ensure an effective, sustainable response to HIV that is consistent with human rights obligations:The first four points are consistent with the 2008 UNAIDS/UNDP Policy Brief recommendations but go further in terms of tone. For example, using "must" rather than "should".
2.1. Countries must not enact laws that explicitly criminalise HIV transmission, HIV exposure or failure to disclose HIV status. Where such laws exist, they are counterproductive and must be repealed. The provisions of model codes that have been advanced to support the enactment of such laws should be withdrawn and amended to conform to these recommendations.
2.2. Law enforcement authorities must not prosecute people in cases of HIV non-disclosure or exposure where no intentional or malicious HIV transmission has been proven to take place. Invoking criminal laws in cases of adult private consensual sexual activity is disproportionate and counterproductive to enhancing public health.
2.3. Countries must amend or repeal any law that explicitly or effectively criminalises vertical transmission of HIV. While the process of review and repeal is under way, governments must place moratoria on enforcement of any such laws.
2.4. Countries may legitimately prosecute HIV transmission that was both actual and intentional, using general criminal law, but such prosecutions should be pursued with care and require a high standard of evidence and proof.
2.5. The convictions of those who have been successfully prosecuted for HIV exposure, non-disclosure and transmission must be reviewed. Such convictions must be set aside or the accused immediately released from prison with pardons or similar actions to ensure that these charges do not remain on criminal or sex offender records.
Point 2.3 on vertical transmission really needs no further explanation and should be implemented immediately.
But what did the Commission mean by some of the recommendations, which, when you read them from the point of view of a legislator, or someone who can affect policy in the criminal justice system, might not be quite as clear as they could be?
And what about point 2.5 recommending that anyone imprisoned for HIV non-disclosure, potential exposure or non-intentional transmission have their case reviewed? Although it doesn't spell out the criteria for review, they should be consistent with the International Guidelines on HIV and Human Rights published by UNAIDS and the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR). Since 1998 they have recommended that in order for someone to be convicted, “the elements of foreseeability, intent, causality and consent [must be] clearly and legally established to support a guilty verdict....” If we now consider that the Commission recommends that only intentional and malicious transmission should be a crime, if the above criteria have not been met (and in most cases they have not), the Global Commission recommends immediate release from prison, a pardon and removal of criminal records (and in the US and Canada, removal from the sex offender registry).
I asked Professor Matthew Weait, who served as a member of the Technical Advisory Group for the Commission (the TAG), with particular responsibility for HIV criminalisation about how we should interpret recommendations 2.1, 2.2 and 2.4 in the real world.
The excellent working paper that he prepared for the Commission, The Criminalisation of HIV Exposure and Transmission: A Global Review is also now available to download. A second paper, Criminalisation and the Moral Responsibility for Sexual Transmission of HIV by Matthew and his fellow TAG member, Professor Scott Burris is also now available.
Q: In 2.1 Does the Commission only recommend repealing laws that explicitly criminalise non-disclosure, exposure or transmission? What, for example, does that mean for Canada, which uses general laws to prosecute non-disclosure?
It's a good question! Before I answer it, can I emphasise that what I say here should in no way should be seen as reflecting the views or interpretation either of other TAG members, the Commissioners, or the UNDP Secretariat that provided logistical and other support. They are personal views. So - with that in mind - I think it's important to read this Recommendation in the context of the Report as a whole. What is abundantly clear is that the Commission believes that only the actual and deliberate transmission of HIV may legitimately be criminalised, and all the Recommendations need to be read in that light. This means, in my view, that countries which criminalise HIV under their general laws are also being addressed here. The reason is that in many such countries it is only HIV transmission, exposure and non-disclosure which is prosecuted in the criminal courts under general provisions which could also be used in the context of other diseases. The fact that other diseases are not, or extremely rarely so, means that HIV is - to my mind - explicitly criminalised. Just because HIV is criminalised under a general law doesn't detract from the fact that such criminalisation is explicit in practice. You'll have to follow this up with the Commission though!Q: In 2.2 Does the Commission mean that law enforcement authorities can prosecute for HIV exposure and non-disclosure where there is proof of intentional or malicious transmission?
I don't think so, no. The "must not" construction of the Recommendation does not imply the opposite, especially where to read it this way would be against the entire tenor of the Report. It is very important, in my view, that law enforcement authorities do not take this as a "green light" – not only because it would lead to over-criminalisation (belt and braces) - but it would serve no purpose.Q: In 2.4 Does the Commission suggest that prosecutions can still take place that aren't malicious? How do you prosecute "with care"?
This Recommendation is in permissive language, similar to that used in the UNAIDS 2008 Policy Guidance, and does not - I think this is important - mandate criminalisation as such. It seems to me to be intended to provide states with a “let out” clause, reflecting the views of many in the wider HIV policy community, and is politically pragmatic and realistic. Some might think it is a unfortunate that this is in a list of Recommendations, but I think I understand why it has been. It might have been better to phrase the Recommendation in the form, “If countries wish to criminalise HIV, they should only do so in cases of actual and intentional transmission”, but I don't think we should get too hung up on the exact language here. As with the other Recommendations, it has to be read in the light of everything else in the Report, where it is clear that Commission is arguing for the most restrictive approach possible. It will also, by the way, be important to see whether the Report itself addresses in more detail what is meant by intentional and malicious. Different jurisdictions interpret these terms is in a variety of ways – some equating them with knowledge of status, some with knowledge of the risk of transmission, and some with deliberate or purposive intent (or a combination of all these). The fact that the Commission uses the term “malicious” in Recommendation 2.2 suggests that it has in mind deliberate and purposive intention
As for question of pursuing prosecutions 'with care', it is clear that the Commission has affirmed what has been emphasised in a number of recent policy documents, including a recent initiative of UNAIDS. The highest (I would personally have preferred that, rather than “high”) is necessary when dealing with liability based on expert evidence (as transmission cases typically are, at least where the scientific analysis facilities are available).
 |
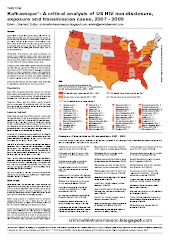
| Catherine Hanssens highlights the problem with US HIV disclosure laws |
This morning, the Global Commission held a press conference that featured several of the Commissioners: US Congresswoman Barbara Lee; Canada's Stephen Lewis (Co-Director and Co-Founder of AIDS-Free World); and His Excellency Mr. Festus Gontebanye Mogae, former President of Botswana.
Three members of civil society also participated: Nevena Ciric, More than Help, AIDS +, Serbia; Maurice Tomlinson, AIDS-Free World, Jamaica and Nick Rhoades, Positive Justice Project, The Center for HIV Law and Policy, United States.
Nick Rhoades spoke with clarity and power about the lessons learned from his own terrible experience. HIV criminalisation wastes money, harms prevention and human rights, he concluded. Return sanity, science and justice to HIV laws.
I was convicted in 2008 under Iowa’s law titled “criminal transmission of HIV” although HIV was not actually transmitted. This involved a one-time, consensual sexual encounter with another adult. My viral load was undetectable, I used a condom – and again, I did not transmit HIV. However, none of these facts mattered in the eyes of the law. The judge imposed the maximum sentence of 25 years in prison and the requirement to register as a sex offender for the rest of my life. After sentencing, the judge was subject to a significant amount of pressure from advocates in the U.S. and even Europe – requesting my sentence be reconsidered. After being incarcerated for over a year, he released me on five years probation, but I am of course, still a sex offender. [Nick is now appealing his conviction.]Following Nick's powerful testminony, much of the rest of the Global Commission press conference mostly focused on HIV criminalisation in the US and Canada - as it should since the vast majority of prosecutions take place in these two countries, a fact highlighted by Stephen Lewis and echoed by Nick Rhoades.
During my course through the correctional system, I transferred facilities four times. Each time I was transferred, I would be either without medications or missing certain medications for a period of days. And when I was released, I had lost my place on the AIDS Drug Assistance Program, so I was put on a wait-list. The correctional system offered no assistance in finding a social worker or medication assistance once I was released from prison.
The personal toll this has taken on me and my family and friends cannot be measured. This has caused great mental anguish, financial burdens and major professional barriers for me, now that I am a sex offender. I have been virtually unemployable. I am fortunate enough now to be employed from home by The Center for HIV Law & Policy, but most aren’t so lucky. To this day, I deal with terrible depression. It’s not easy.
What’s more, the price to enforce these archaic laws is considerable. The approximate cost to tax-payers to incarcerate just one individual in Iowa – factoring in the cost of medications and routine medical care is approximately sixty-five to seventy thousand dollars annually. This cost is borne by tax-payers and doesn’t include the lost income and contribution to society that incarceration causes. Then consider the price to supervise people convicted under these laws while on probation or parole – often being forced to add in the costs of monitoring offenders on the sex offender registry – and the public is paying an incredible amount of money for enforcing laws that, more often than not, are punishing people for not transmitting HIV. In many cases, such as mine, taxpayers are paying for the enforcement of laws that punish people with HIV who actually follow the primary prevention messages of public health counselors: stay in treatment, keep your viral load as close to undetectable as possible, use condoms – and otherwise, keep sex safe[r].
These laws enhance stigma that cripples people living with HIV/AIDS from accessing services. They make disclosure issues much more difficult due to ramifications one may face with a mere accusation. I also believe stigma, made thicker by these laws, is keeping people from getting tested.
Furthermore, I have been a member of the Iowa HIV Community Planning group – chaired by the Iowa Department of Public Health – since 2009. I see all the data. This year, the Iowa Department of Public Health’s prevention-based budget faced a 25% decrease which will eventually grow to 55% over the next five years. Dollars marked to treat people in care are next for slashing. Those in care and with undetectable viral loads are up to 96% less likely to transmit the virus, yet we are cutting funding away from proven HIV prevention programs while increasing costly prosecution and imprisonment of people like me living with HIV. When one considers that there is no evidence that these laws have any impact on people’s sexual behaviors, it is clearly not an effective use of our resources while infringing on individuals’ human rights and working in conflict with public health goals.
Criminal laws and policies that target people based on their HIV status must be repealed. Please support Congressperson Barbara Lee’s “Repeal HIV Discrimination Act” now, and engage with those who are promoting the movement to return sanity, science and justice to the law’s treatment of HIV.
 |
| I was very honoured to be quoted in the report. |
I asked Rep. Barbara Lee how it is posssible to change these bad laws when it appears that they have popular support. "Modernising these laws won't be easy," she said. "But I have to tell you that the public isn't really aware of these laws. Once you explain it to them, they're shocked. What we have to do is mount public education campaigns about these laws. At state level, many state legislators don't know these laws are on the books, and they can change them if there is the political will. So we need public and political education and civil society support for a political movement to hold politicians accountable. But... yes we can!"
As for other countries using general criminal laws to prosecute non-disclosure, potential exposure and transmission, in the next few months UNAIDS will be releasing a policy consideration document that will help countries understand exactly how to limit their application through a better understanding of HIV science as well as public health and human rights principles.
There's going to be a lot more happening around the Global Commission's Report and all of the amazing evidence the Commission accrued during it's two year existence. I recommend spending time on the Global Commission website where you will now find a treasure trove of documents to help further anti-criminalisation advocacy and eventually lead to HIV justice for all.